We recycle waste by using
an electric arc furnace.
Waste is recycled by being melted in an electric arc furnace (EAF) together with scrap metal, which is the main raw material.
After such processing, the metallic portion is completely material recycled,
and the remaining portion is thermally recycled to recover and use the generated energy.
Thus, ideal resource recycling with near-zero residue is achieved.
Benefits of recycling by our company
-
Effective
The rate of recycled useful
resources is over 99%. -

Clean
A clean melting treatment that satisfies the environmental
standard is achieved. -
Economical
A treatment excelling in cost is achieved
with the use of an EAF.
Effective
Effective
Recycling of
waste batteries
Iron, manganese dioxide, zinc, and carbon,
which are the main components of alkaline manganese dry batteries, are all valuable resources.
Our company recycles the valuable resources contained in waste batteries on a 100% basis.
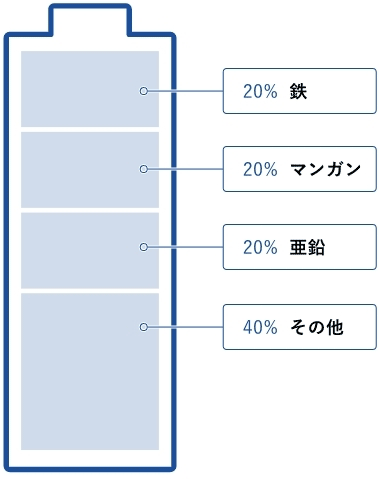
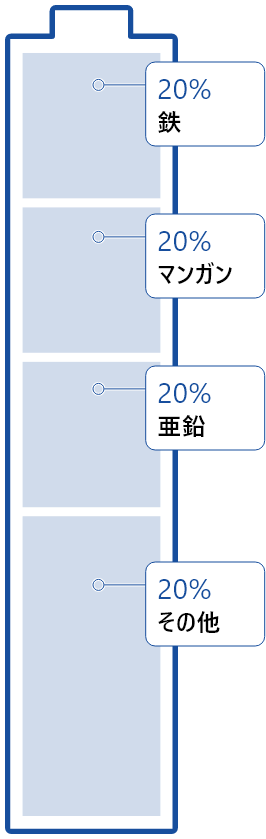
- Steel in the metal jacket is melted, and then recycled as a steel product.
- Manganese in the positive electrode is partially recovered as an alloy element in steel, making the steel more resilient.
- Zinc in the negative electrode is evaporated, the vapor is collected using a dust precipitator, and then recycled as zinc ingots at a zinc refinery.
- The carbon component in the positive electrode helps recover manganese into steel by reducing the manganese oxide. The other components are also appropriately treated in the ultra-hot EAF, and no residue is produced.
Clean
Economical
Mechanism of recycling
Our company conducts clean and low-cost recycling through the EAF fusion process.
Since this process is material recycling in which the material
is instantaneously melted and detoxicated by ultraheat treatment, no residue is produced.
In addition, we conduct thermal recycling in which thermal energy is recovered and used.
Ultraheat complete fusion process using an electric arc furnace
All materials are completely fused in an electric arc furnace. The molten steel is effectively used into a steel product, the slag into a base course material, the dust into a raw material for zinc refining, etc.
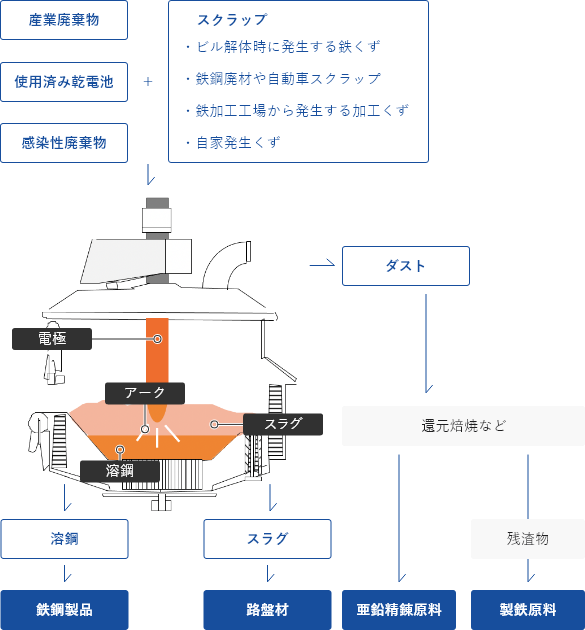
Two types of recycling are in operation.
・Complete material recycling for metallic components (Fe, Mn, etc.)
・Highly efficient thermal recycling of raw materials for energy
- ① Charging into an EAF
Waste is charged into an
EAF together with scrap metal,
which is the main raw material. - ② Melting and refining
(waste melting)
Waste and scrap are melted
and detoxicated at ultra-high temperature.
Molten steel is recycled into a steel product. - ③ Removal of slag
Slag, which is removed during refining,
is also effectively used for example
as a base course material. - ④ Recovery of dust
Dust captured by a dust collector
is also effectively used for example
as a raw material for zinc refining.
Ultraheat complete fusion process using an electric arc furnace
All materials are completely fused in an electric arc furnace. The molten steel is effectively used into a steel product, the slag into a base course material, the dust into a raw material for zinc refining, etc.
- Charging into an EAF
Waste is charged into an EAF together with scrap metal,
which is the main raw material.

- Melting and refining (waste melting)
Waste and scrap are melted and detoxicated at ultra-high temperature. Molten steel is recycled into a steel product. - Removal of slag
Slag, which is removed during refining, is also effectively used for example as a base course material. - Recovery of dust
Dust captured by a dust collector is also effectively used for example as a raw material for zinc refining.
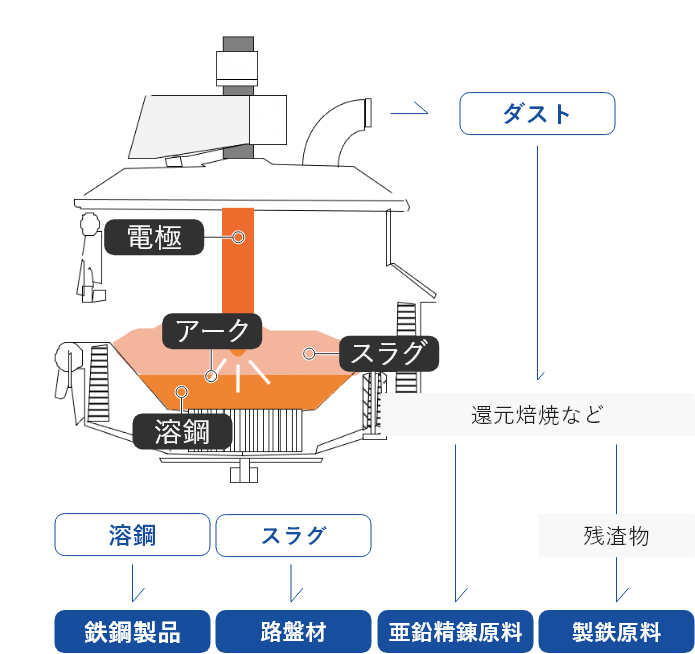
Two types of recycling are in operation.
・Complete material recycling for metallic components (Fe, Mn, etc.)
・Highly efficient thermal recycling of raw materials for energy
Information on treatment of general
waste and industrial waste
In 2002, we launched a resource-recycling business at
our Mizushima Works as one of the earliest companies as EAF company,
taking advantage of the technology, experience, and know-how we have cultivated through EAF refining.
Currently, we also conduct waste treatment at our Kashima Works,
and are seeking to expand our resource-recycling business.
Mizushima Works
Facility installation permit
| Industrial waste | General waste | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Permitter | Kurashiki City | Kurashiki City | |
| Scope of business | Intermediate processing (incineration) | - | |
| Type of Facility | - | Waste-processing facility (incinerator) | |
| Permit No. | No. 10020165583 | No. 100004 | |
| Date of permit | April 8, 2022 | November 2, 2015 | |
| Expiration date of permit | March 31, 2027 | - | |
| Processing capacity | 540 t/day (540 t x 1 unit) | - | |
| Processing facility | - | DC electric arc furnace (1 unit), dust collector (1 unit) Air flow: 374,000 Nm3/hr |
|
| Type of waste | Cinder, sludge, scrap metal, scrap glass, scrap concrete, scrap ceramics, slag, debris, soot and dust, waste plastics, scrap paper, scrap wood, woodchips, scrap fiber | Waste batteries, waste spring mattresses |
State of maintenance and management
Outline of
the facility
| Name of processing facility | Unit 2 electric arc furnace |
|---|---|
| Type of measurement | (1) Measurement of the concentration of smoke and soot in exhaust gas (2) Measurement of the concentration of dioxin in exhaust gas |
| Measuring position | (1) Dust collector outlet for each EAF |
| Items and units of measurement | (1) Smoke, soot, and dust: g/Nm3
NOx: ppm
SOx: ppm
HCL: mg/m3 (2) Dioxin (electric arc furnace standard) dioxin concentration: ng/Nm3 |
Maintenance management value
- Result of measuring of the smoke, soot, and dust in exhaust gas (latest measurement result)
- Date of sampling: March 2024
Soot and dust: 0.003 g/Nm3
NOx: 18 ppm
SOx: 3.9 ppm
HCL: 0.2 mg/m3 - Result of measuring of the concentration of dioxin, etc. in exhaust gas (latest measurement result)
- Date of sampling: January 2025
Dioxin concentration: 0.00014 ng-TEQ/Nm3
Maintenance and management values of waste processing facilities (EAFs)(Japanese)
Kashima Works
Facility installation permit
| Industrial waste | General waste | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Permitter | Ibaraki Prefecture | Ibaraki Prefecture | |
| Scope of business | Intermediate processing (incineration) | - | |
| Type of Facility | - | Waste-processing facility (incinerator) | |
| Permit No. | No. 00821165583 | No. 1-145 | |
| Date of permit | December 5, 2022 | July 6, 2022 | |
| Expiration date of permit | December 4, 2027 | - | |
| Processing capacity | 220t/day (220 t ×1 unit) | - | |
| Processing facility | - | DC electric arc furnace (1 unit),dust collector (1 unit) Air flow: 240,000 Nm3/hr |
|
| Type of waste | Cinder, sludge, waste plastics, scrap metal, scrap glass, scrap concrete, scrap ceramics, slag, debris | Waste batteries, waste spring mattresses |
State of maintenance and management
Outline of the facility
| Name of processing facility | Unit 2 electric arc furnace |
|---|---|
| Type of measurement | (1) Measurement of the concentration of smoke and soot in exhaust gas (2) Measurement of the concentration of dioxin in exhaust gas |
| Measuring position | (1) Dust collector outlet for each EAF |
| Items and units of measurement | (1) Smoke, soot, and dust: g/Nm3 NOx: ppm SOx: ppm HCL: mg/m3 (2) Dioxin (electric arc furnace standard) dioxin concentration: ng/Nm3 |
Maintenance management value
- Result of measuring of the smoke, soot, and dust in exhaust gas (latest measurement result)
- Date of sampling: February 2025
Soot and dust: 0.012 g/Nm3
NOx: 3 ppm
SOx: <0.1 ppm
HCL: <1 mg/m3 - Result of measuring of the concentration of dioxin, etc. in exhaust gas (latest measurement result)
- Date of sampling: January 2025
Dioxin concentration: 0.035 ng-TEQ/Nm3
Maintenance and management values of waste processing facilities (EAFs)(Japanese)
CONTACT
If you have any questions or requests or seek our advice,
please ask us at the following contact.

Waste processing at JFE Bars & Shapes